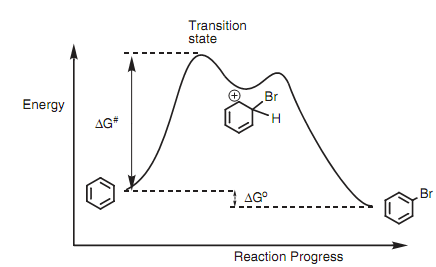
Bromination Of Acetone Activation Energy
Learn more about these metrics Article Views are the COUNTER-compliant sum of full text article downloads since November 2008 (both PDF and HTML) across all institutions and individuals. These metrics are regularly updated to reflect usage leading up to the last few days. The Altmetric Attention Score is a quantitative measure of the attention that a research article has received online. Clicking on the donut icon will load a page at altmetric.com with additional details about the score and the social media presence for the given article. Find more information on.
= k [acetone] 0 [HCl] 0. Once the rate law expression is found, the activation energy of the reaction is found by measuring the rate of the reaction at multiple temperatures. The Hunger Games Book 1 Audiobook Free Download. The calculated activation energy of 92 ± 11 kJ/ mol is sufficiently large to make the reaction slow enough to observe, but not so large as to make the reaction exceedingly slow. Bromination Of Acetone Activation Energy. Vinyl Siding Assn Installation Manual Online more. 5/31/2017 0 Comments Oriental Journal of Chemistry is a peer reviewed quarterly research journal of pure and applied. Estimation of the Activation Energy for the Iodination of Acetone Through the Effect of Temperature on the Rate Constant Joel Costa, Alex Fuentes, Michael.
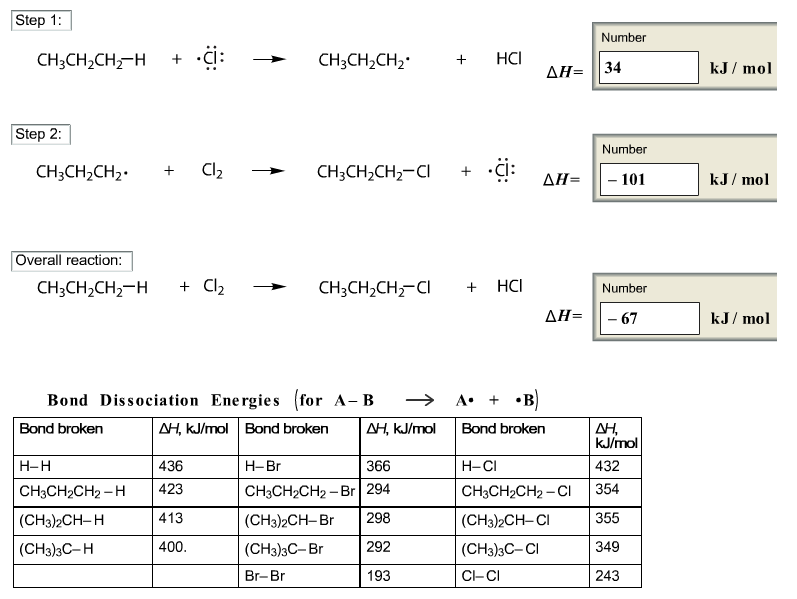
Reaction Kinetics. Splinter Cell Chaos Theory Free Download For Android here. The Bromination of Acetone1REFERENCES Chapter 25 Chapter 17Physical Chemistry, Atkins, 1994Physical Chemistry, Levine, 4th edition 1995PURPOSE:The purpose of this experiment is to determine the rate law and the rate constant for thebromination of acetone. From rate data collected at two or more temperatures, theactivation energy is determined.DISCUSSION:The bromination of acetone in acid solution proceeds according toCH3C(O)CH3 + Br2 H+ → CH3C(O)CH2Br + Br– + H+ [1.]The reaction is catalyzed by hydrogen ion.
Halogenation of acetone. A method for determining pKas of ketones in aqueous solution, with an examination of the thermodynamics and kinetics of alkaline halogenation and a discussion of the best value for the rate constant for a diffusion-controlled reaction.
The rate law is assumed to be of the formrate − d[acetone] − d[Br2 ] k[acetone]p[Br2 ]q[H+ ]r [2.] dt dt = = =where k is the rate constant and [A] represents concentration of A in moles liter-1. Theexponents p, q, and r indicate the order of the reaction with respect to acetone, bromine,and hydrogen ion, respectively.The bromination of acetone is a particularly convenient and interesting reaction to studykinetically. The progress of reaction is readily followed by directly observing thedecrease in bromine concentration spectrophotometrically at a wavelength where noneof the other reagents has significant absorption. Further, the reaction provides aremarkable demonstration of the general rule that it is not possible to predict the ratelaw from just the knowledge of the stoichiometric equation. As will be confirmed inthis experiment, the reaction is zero order in bromine, i.e., q in equation [2] is zero.This result provides a straightforward application of the method of initial rates whereinthe acetone and acid are present in large excess while the bromine is used in smallconcentrations to limit the extent of reaction. The small amount of bromine iscompletely consumed while the other reactants remain at an essentially constantconcentration.